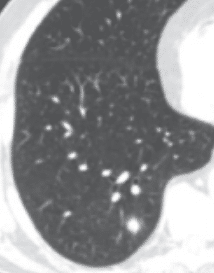
56-year-old woman is 5 months post kidney transplant. She has had a fever and cough for 4 days and has received antibiotics.
The cause of the recipient’s end-stage kidney disease is diabetic nephropathy. The patient had delayed graft function. Both the kidney donor and the recipient were cytomegalovirus seropositive. Blood studies are ordered. The CT scan of the chest is offered above to help provide the diagnosis. Pulmonary nodules with surrounding low attenuation are noted.
Please answer the following questions:
What is the most probable infectious agent responsible for this patient’s fever?
* Aspergillus
* Pneumocystis jirovecii
* Cytomegalovirus
* Rhizopus arrhizus
Aspergillus
CT scan of the lung reveals pulmonary nodules with surrounding low attenuation (“halo sign”) suggesting the diagnosis of aspergillus.
What is one of the major risk factors for invasive aspergillosis in renal transplant recipients?
A
Older age
B
Regular exercise
C
High blood pressure
D
Low levels
A
Older age
Which type of infection is the most common in invasive aspergillosis cases?
A
Urinary tract infection
B
Skin infection
C
Parenchymal pulmonary infection
D
Ear infection
C
Parenchymal pulmonary infection
When do about 50% of invasive aspergillosis cases occur after renal transplantation?
A
1 year
B
2 years
C
First 6 months
D
5 years
C
First 6 months
What is one of the fastest means of establishing the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis?
A
Urinalysis
B
Blood culture
C
Serum Aspergillus antigen test
D
X-ray imaging
C
Serum Aspergillus antigen test
Which medication is NOT recommended as standard therapy for invasive aspergillosis?
A
Isavuconazole
B
Liposomal amphotericin B
C
Voriconazole
D
Posaconazole
B
Liposomal amphotericin, because it is a less effective treatment option.
Discussion:
More Nephrology for You:
Related: Diarrhea After Recent Kidney Transplant – Provider Quiz – Nephrology
Assessing CAD In ESRD – Transplant Evaluation, Quiz With Solution by Michael Aaronson, Lincoln Nephrology and Hypertension