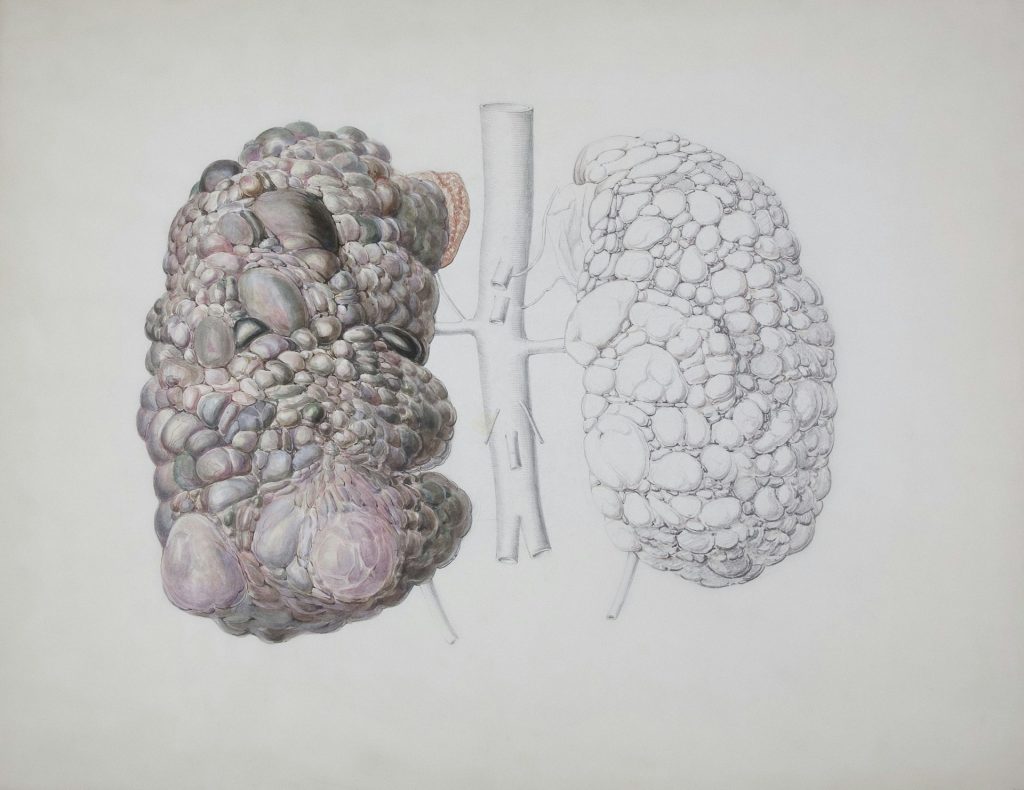
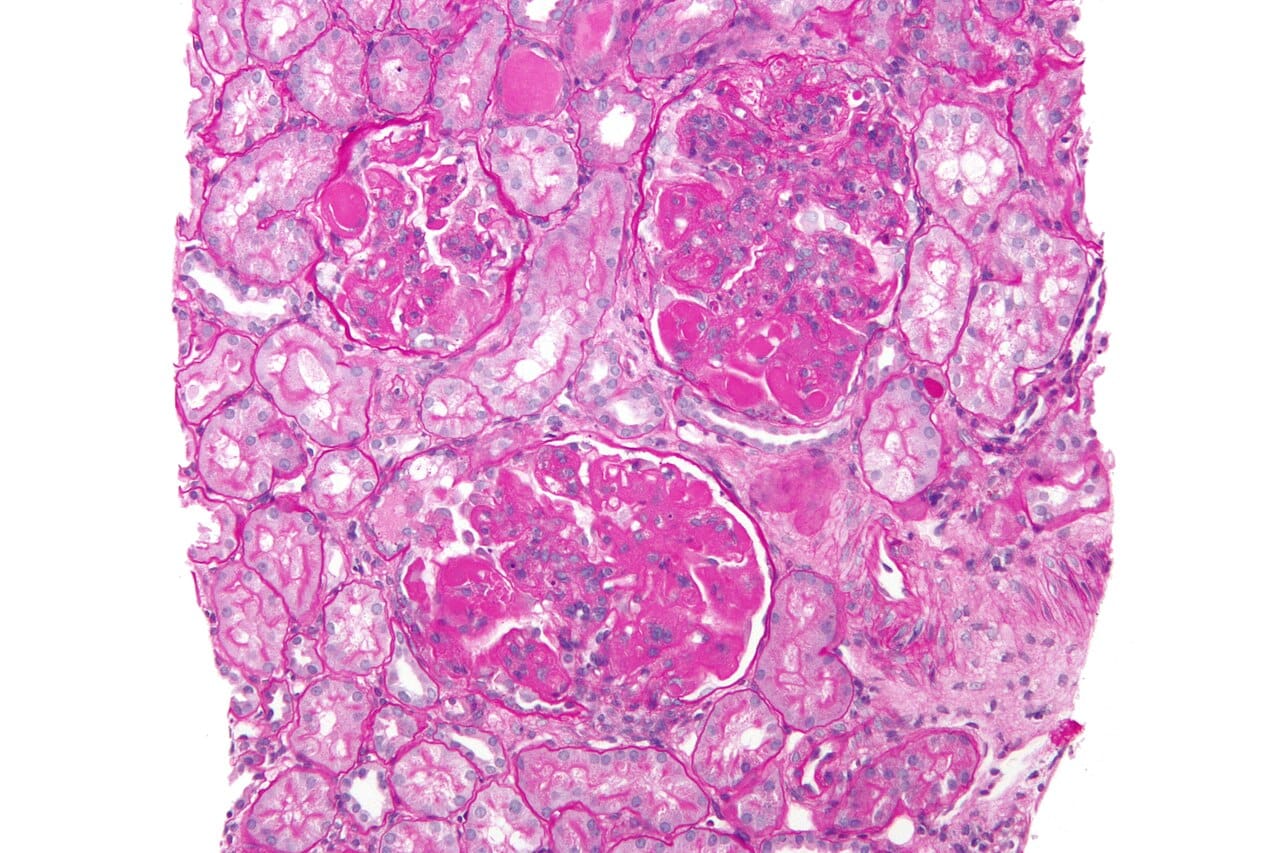
The importance of total kidney volume:
A 25-year-old white male patient presents to the clinic with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and CKD 2. His creatinine level is 1.5. His uACR is less than 30. He is 5 foot, 10 inches tall.
Multiple relatives across three generations have been diagnosed with ADPKD and have progressed to End-Stage Kidney Disease. Some have received a kidney transplant.
The patient has had ultrasounds of his kidneys in the past. And he has been told that the cysts are growing in size. The patient is concerned.
The nephrologist mentions to the patient that the continued enlargement of cysts in ADPKD is a major factor in the development of kidney failure. Even though the creatinine is 1.5, the patient should not think that all will go well, because the CKD stage is not the strongest predictor of future kidney failure. It is the size of the kidneys, the total kidney volume, that predicts future kidney function.
The patient asks his nephrologist if there is a simple method to predict his future kidney function in 5-years.
The nephrologist has noted that the Mayo Clinic Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease classification scoring system, which measures total kidney volume using either a CT scan, MRI, Kidney Volume Calculator, or previous Stereology, can predict the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in 5 years. This method will allow a way to determine prognosis and, if desired, follow the progression of the patient’s CKD.
The patient consents to total kidney volume and has a CT scan done to get sagittal length, coronal length, width, and depth of both the right and left kidneys. Plugging in the numbers, his total kidney volume calculates to 1808 ml/m.
Please answer the following questions using the ADPKD Classification, Mayo Clinic Prediction Tool. Accept the terms to access the calculator. It’s free.
What is the patient’s height adjusted total kidney volume using 1808 ml/m as the total volume measurement? Hint: use the third option of the table and the following variables: Kidney Volume in ml, 1808.2, convert patient height to meters, 1.7, Patient Age in years is 25.
If you need help with the calculation, use the height converter to convert feet to meters.
The patient’s height adjusted total kidney volume is 1063 ml/m.
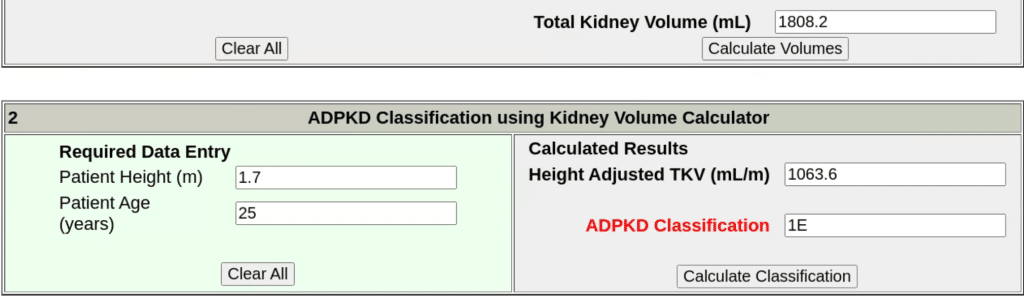
Plug in the numbers and then press calculate to get the answer shown.
Assuming the patient has a height of 1.7 meters (5 foot, 10 inches) and is 25 years old, what is the patient’s ADPKD classification?
1E. The computation has already been completed above (see previous question). This question highlights the severity of the patient’s autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease shown in the figure below.
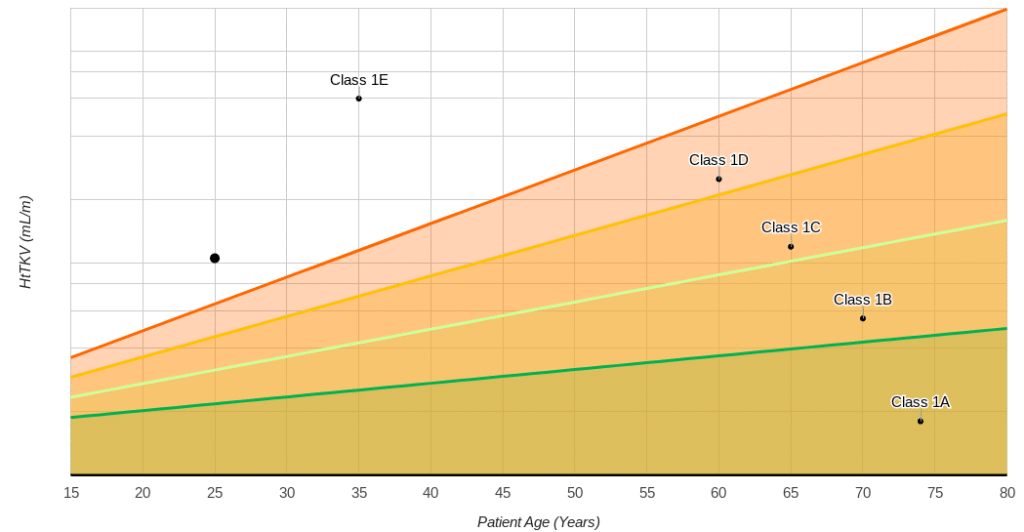
The patient, categorized as a Class IE, is at the highest risk of progressing to End-Stage Kidney Failure.
We should focus on therapies to mitigate risk, which include increased fluid intake, dietary sodium restriction, aggressive blood pressure management, and possibly competitive vasopressin receptor 2 antagonists. We should also consider goal directed kidney strategies to optimize this patient’s care. This patient may need a kidney transplant or dialysis in the future. An estimation of future eGFR can help us here. The involvement of a nephrologist as part of the team can be helpful in this setting.
Predict the future eGFR in 5 years noting: serum creatinine 1.5, age 25 years, race white, gender male, ADPKD classification 1E:
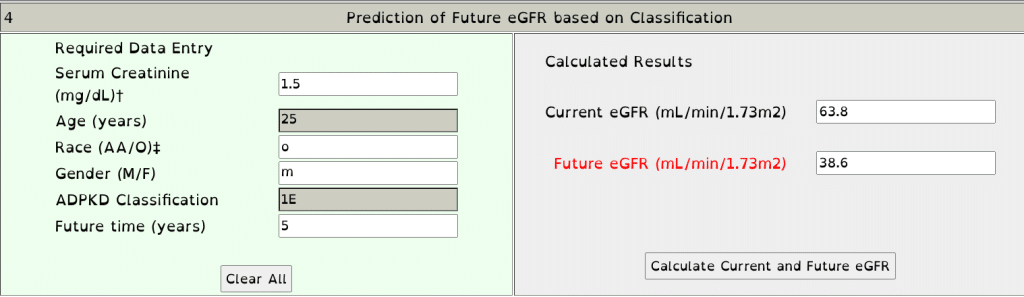
The patient currently has an eGFR of 63.8, CKD stage 2.
In 5 years, it is predicted the patient will have an eGFR of 38.6, CKD stage 3B
Let us evaluate his prognosis another way using the CKD heat map:
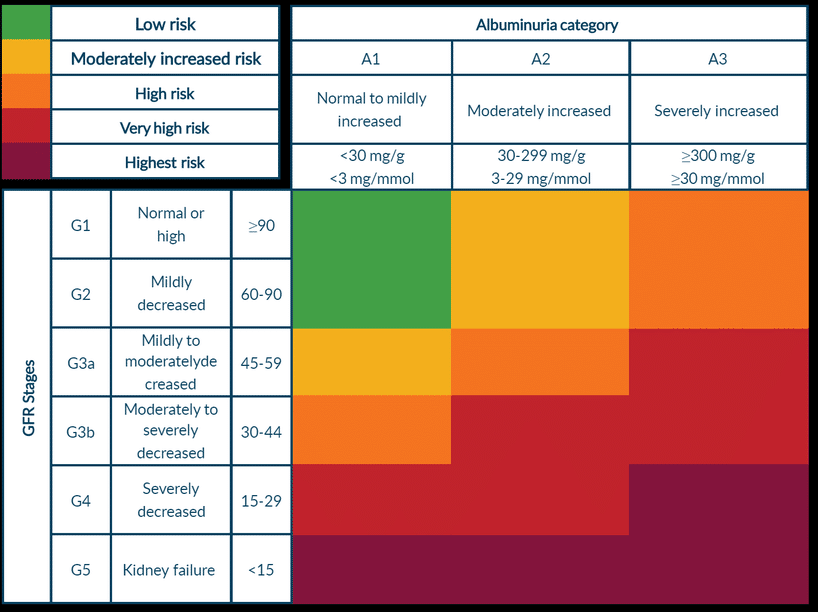
The patient will progress from CKD 2 (green) to CKD 3B (orange) in 5 years and be at high risk. He will be 30 years old.
Discussion:
Related: