A patient comes to the nephrology clinic for a work-up of kidney stones. He has a history of tophi and chronic painful arthritis.
He shakes your hand. See the following picture:
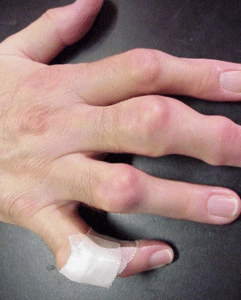
When you shake the patient’s hand, you notice tophi
He then presents you with the stones he has been frequently forming. See the kidney stones the patient has been forming.

Please answer the following questions:
What type of stone does this patient most likely have?
Uric acid nephrolithiasis.
The patient has tophi. Tophi are deposits of uric acid crystals that build up in joints because of hyperuricemia or elevated levels of uric acid. Tophi are often linked to gout and appear as bumps under the skin as shown above. These lumps present near the fingers, toes, and other joints.
What are tophi in the context of gout?
A
Fluid-filled sacs around joints
B
Calcium deposits in the bones
C
Solid chalky white masses of uric acid
D
Inflammatory cells in the bloodstream
C
Solid chalky white masses of uric acid
Given the following options, where do tophi typically form in the body with a predilection?
A
Extensor surfaces of the elbows
B
Back muscles
C
Abdominal organs
D
Lower back vertebrae
A
Extensor surfaces of the elbows
How do tophi affect bone health?
A
They promote bone growth
B
They strengthen bone density
C
They can directly erode bone
D
They have no impact on bones
C
They can directly erode bone
How can uric acid kidney stones be dissolved in most cases?
A
Increasing uric acid levels
B
Decreasing urinary pH
C
Decreasing hyperuricosuria
D
Increasing urinary pH and volume
D
Increasing urinary pH and volume
Discussion:
Related Posts:
Kidney Stone Quiz – Urine Provided – What Type Of Stone Am I Making?