56-year-old woman has returned from a vacation to mainland Southeast Asia. Her primary ordered mefloquine prophylaxis for plasmodium falciparum malaria, which the patient adhered to during the trip. The patient has had a splenectomy in the past.
The patient presents to the hospital with confusion, a fever to 104 F, hypotension with a blood pressure of 89/61, and pulmonary edema on the CXR.
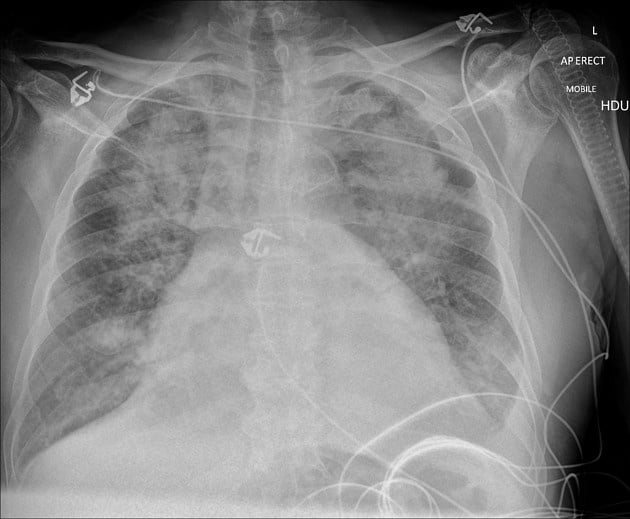
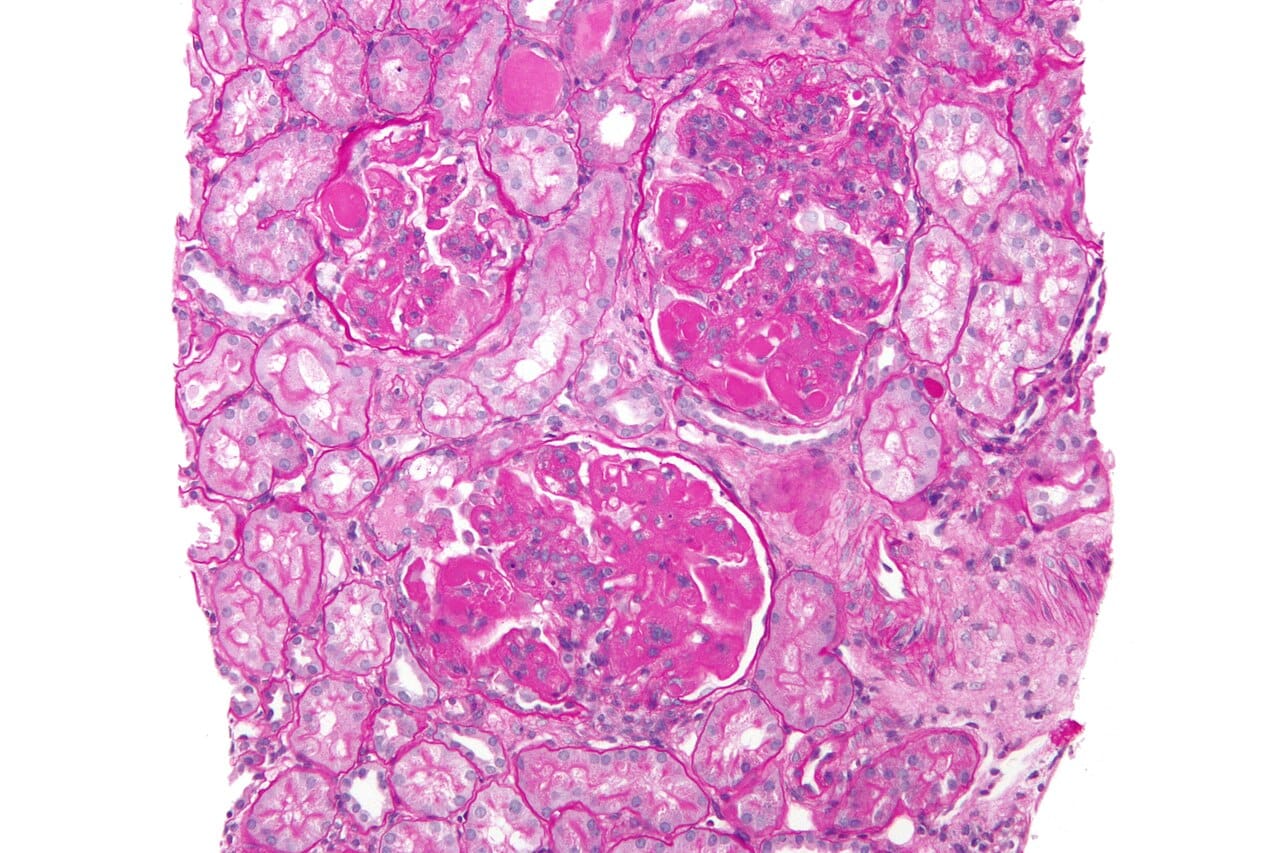
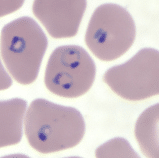
Labs show AKI on CKD 3B with a serum cr of 3.4 (baseline cr 1.8). The hemoglobin is 8.3. Urinalysis reveals blood with 0-3 rbc on microscopy. The peripheral blood smear is shown above.
Please answer the following questions:
What is the treatment of choice?
* Primaquine
* Artesunate
* Atovaquone-proguanil
* Tafenoquine
Artesunate
With severe malaria, the recommended approach is to start treatment with intravenous artesunate, followed by a switch to an oral antimalarial regimen once the patient’s condition has stabilized.
Describe the distinctive morphologic characteristics of Plasmodium falciparum species on a peripheral blood smear
There are thin, often multiple rings on the inner surface of young and old erythrocytes, as well as banana-shaped gametocytes.
Plasmodium falciparum is known for its unique appearance on a blood smear because of the presence of thin rings in both young and old red blood cells. The banana-shaped gametocytes distinguish this species. These characteristics aid in the identification of P. falciparum during microscopic examination.
Define severe malaria primarily associated with Plasmodium falciparum.
Defined by high parasitemia (>10%) along with clinical (e.g., pulmonary edema, seizures, confusion) and laboratory (e.g., severe anemia, acute kidney injury, hypoglycemia, hemoglobinuria, metabolic acidosis) criteria.
How does splenectomy affect the risk of severe disease in malaria infection?
increases the risk as the spleen filters and clears malaria-infected erythrocytes.
Splenectomy increases the risk of severe disease in malaria infection because the spleen plays a crucial role in filtering and clearing malaria-infected red blood cells from the circulation. Without a functioning spleen, the body’s ability to control the infection is compromised, leading to a higher risk of severe complications.
Describe the regions where mefloquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria is increasingly prevalent.
Various parts of Southeast Asia, including Laos and Cambodia, are included in the regions where mefloquine-resistant Plasmodium is increasingly prevalent.
Mefloquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria is a growing concern in Southeast Asia because of the spread of drug-resistant strains. Countries like Laos and Cambodia have reported increasing prevalence, highlighting the urgent need for effective malaria control strategies in these regions.
What intensive medical care measures are immediately required for severe malaria cases?
Hemodynamic and respiratory support, fluid and electrolyte management, blood replacement, and potentially hemodialysis can help the patient during this time.
Severe malaria cases can lead to life-threatening complications like organ failure. Hemodynamic support stabilizes blood flow, while respiratory support ensures proper oxygenation. Managing fluids and electrolytes helps maintain balance. Blood replacement and hemodialysis may be necessary for severe cases with complications.
Do atovaquone-proguanil and quinine sulfate treat all malarial species, regardless of chloroquine sensitivity?
Yes, they can treat all malarial species.
Define hypnozoites in the context of malaria
Hypnozoites are the latent hepatic stage found in P. vivax and P. ovale.
Hypnozoites are dormant liver forms of the Plasmodium parasites, specifically P. vivax and P. ovale. They can remain inactive for extended periods before reactivating, causing relapses of malaria. Treatment targeting hypnozoites is crucial for preventing these relapses.
How are primaquine and tafenoquine used in malaria treatment?
They are given after treating the erythrocytic stage to prevent clinical relapse by eradicating persistent liver infection.
Primaquine and tafenoquine are used in malaria treatment to target the liver stage of the parasite’s life cycle, preventing relapse. They are particularly effective against Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale malaria strains due to their ability to eliminate dormant liver forms of the parasite.
Discussion:
Related Posts: