Background:
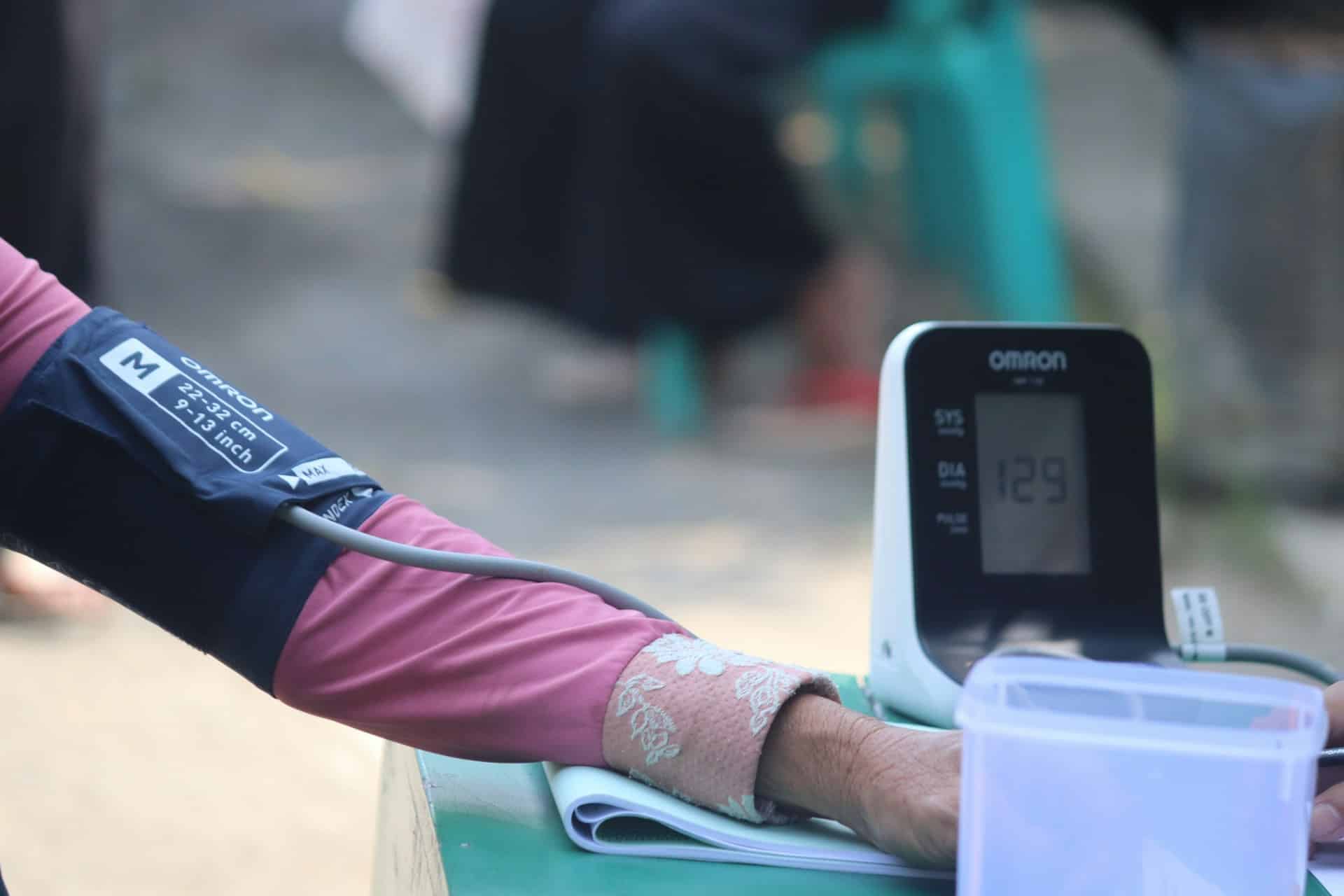
48-year-old female presents with systemic sclerosis and hypertension. Her blood pressure is 200/105. She just got back from a trip and was given antibiotics and prednisone for bronchitis at an urgent care. The patient is currently taking 20 mg of prednisone. She also notes a headache. Her physical exam reveals thickened skin. The head CT scan was normal.
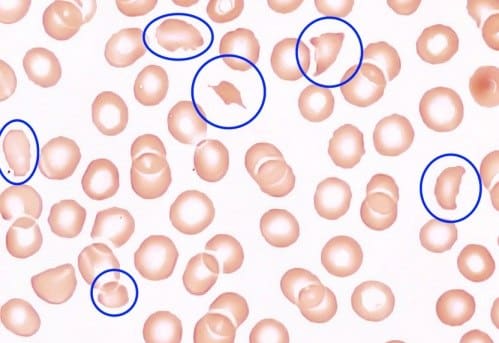
She gets admitted to the hospital for hypertensive emergency. Her blood reveals that she is anemic; hemoglobin is 10.5. She is found to have schistocytes on the peripheral blood smear (suggesting microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, shown in the figure above). Her creatinine is 1.8 (baseline 1.3), and she is diagnosed with acute kidney injury (AKI). The urinalysis has protein and blood. The urine microscopy shows 0-2 red blood cells. Anti-RNA polymerase III antibody is positive.
Please answer the following questions:
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
* Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
* Migraine
* Scleroderma renal crisis
Scleroderma renal crisis
Patients with scleroderma renal crisis are typically normotensive.
A
True
B
False
False
Anti-RNA polymerase III antibody has no association with renal crisis in systemic sclerosis.
A
True
B
False
False
Prednisone doses greater than 7.5 mg/d should be avoided in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis to prevent renal crisis.
A
True
B
False
True
Discussion:
Related:
Plasmodium Falciparum With AKI: Treatment – Hospital Medicine Quiz